URASHIMA8000
Overview
Deep Sea Cruising AUV URASHIMA is an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) that operates without any cables connected to a surface vessel. Once a “scenario” ― including parameters such as latitude, longitude, and depth ― is set in advance, the vehicle follows this scenario and autonomously navigates while collecting data such as seafloor topography along the way. Development of the early model began in 1998, and after several modifications and system upgrades, URASHIMA has been used for various deep-sea research. Operating close to the seafloor allows it to acquire high-resolution data on seabed topography and sub-seafloor structures, surpassing the resolution of ship-based surveys.
In 2022, a major upgrade project was launched to extend URASHIMA’s operational depth to 8000 m. In 2025, AUV “URASHIMA8000” successfully completed a test dive in ultra-deep water at a depth of 8000 m. It is expected to be used in the near future for detailed surveys in trench areas including seismic research.

'URASHIMA8000' navigation
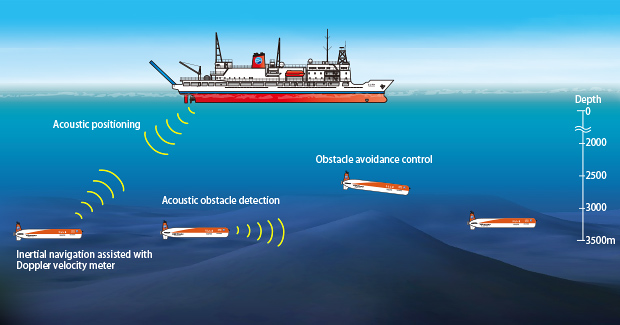
GPS, used everywhere on land, cannot be used underwater because radio signals do not penetrate water. Therefore, once the AUV reaches the seafloor, its position is updated by acoustic communication from the research vessel. Once AUV URASHIMA8000 has accurately determined its position at the departure point, it uses inertial navigation equipment mounted on the AUV to keep track of where it is on the observation line as it navigates.
Furthermore, as the research vessel navigates while measuring its distance (altitude) from the seafloor, it can maintain a constant altitude from the seafloor surface even when there are undulations on the seabed. This is because AUV URASHIMA8000 grasps sensor values from a Doppler groundspeed indicator mounted on the bottom of the AUVs to quickly detect changes in terrain and control the AUVs accordingly.

URASHIMA8000 combines the inertial and acoustic navigation schemes when cruising.
Key Features
Obtaining high-resolution seabed topography and sub-seabed geological structure data
For example, when the altitude from the sea floor is maintained at around 120 m, seabed observations with a resolution of approximately 1 m or less can be made. At the same time, structural data can be acquired down to several tens of metres below sea floor.

Large-sized observation equipment can also be mount
AUV URASHIMA8000's payload space (space for researchers to bring in sensors and other survey equipment) is located at the front and rear of the AUV. As for the front section, it has a capacity of nearly 750 L and can accommodate relatively large equipment such as water sampling equipment and magnetometers.
High data-rate acoustic communication integrated with acoustic positioning
Information can be exchanged between the AUV and mothership by means of acoustic communication. The AUV regularly sends information such as battery level, target point, and depth (altitude) to the mothership. The mothership can also send instructions to the AUV to change scenarios, start or stop observations and adjust settings.
URASHIMA8000 is equipped with an integrated acoustic communication and positioning system developed by JAMSTEC. This system enables stable, frequently updated communication and positioning. It uses the same high-data-rate acoustic communication technology developed for SHINKAI6500, allowing side-scan sonar data to be transmitted directly from the AUV to the mothership. This enables immediate and detailed follow-up surveys of any interesting features discovered during a dive.
For details on underwater acoustic communication devices, please see below.
https://www.jamstec.go.jp/engd/e/uatrg.html
Specifications
General arrangement
History of URASHIMA8000
- July 2025Achieved a diving depth of 8015.8 m in the Izu-Ogasawara Trench.
- Apr 2022Modifying started with the aim of achieving a submerged depth of 8,000 metres.
- Jan 2016The support vessel YOKOSUKA was renovated to carry both URASHIMA and SHINKAI 6500 together. URASHIMA dived the Indian Ocean during the first cruise with SHINKAI 6500.
- Jun 2012The control, propulsion, and inertial navigation systems were replaced with new ones.
- May 2010Received the Performance Award of the Advanced Marine Science and Technology Society.
- Jun 2009JAMSTEC began to accept applications from both JAMSTEC and external researchers seeking the use of URASHIMA. The first dive for an applied research project was in the Mariana Trough.
- Dec 2006Received the First Prize in the Public and Frontier Robot category of the Robot Award of the Year 2006 organized by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and The Japan Machinery Federation.
- Jul 2006Conducted a detailed bathymetric survey on mud volcanoes in the Kumano Trough. The survey was expected to contribute to researches into large-scale earthquakes in ocean trenches as well as methane hydrate resources.
- Jun 2006Succeeded in gathering evidence of submarine landslides and recording detailed seafloor typography off the eastern coast of Izu Peninsula.
- Feb 2005Achieved a new distance world record for cruising vehicles of 317 km.
- Jun 2003Achieved a new world record for continuous cruising distance of 220 km, using a fuel cell.
- Aug 2001Achieved a new world record for AUVs' diving depth of 3,518 m, and succeeded in transmitting video images through acoustic telemetry from that depth.
- Dec 2000Succeeded in the acoustic transmission of color images taken by the onboard camera at a depth of 1,753 m in the Suruga Bay. It was a new world record for AUVs' acoustic transmission distance.
- Apr 1998Development of the deep-sea cruising AUV URASHIMA began with the aim of commencing its practical use in 2005.