1. Carbon cycle model, carbon cycle and climatic change joint modelResults Page | Top Page |
||||||
1-1. Terrestrial carbon cycle modelThe organization in charge: Earth frontier research system
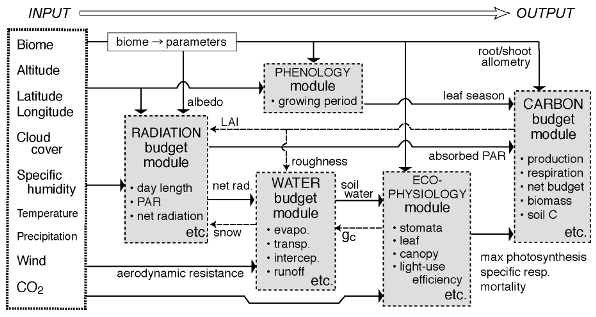
a. Summaryair CO2 concentration -- a short period -- the carbon balance of a terrestrial ecosystem which has long-term influence is presumed, and the ecosystem dynamic model which forecasts the leaf area index (LAI) which is an index representing the amount of functions of a terrestrial ecosystem is built. The frame of the ecosystem model based on Sim-CYCLE was created, and the response simulation by off-line was performed simultaneously in FY 2002. b. Research purposeThe photosynthesis and breathing by a terrestrial ecosystem reach annual 100-120 Pg C, and have the greatest scale in the carbon flaw which participates in the atmosphere CO 2. If a serious change occurs in a terrestrial ecosystem function by the present earth environment change, there is a hypothesis of change arising also within CO2 income and outgo between air-terrestrial, and changing the speed of advance of future climate warming intentionally, but examination has actually begun already by some pioneering model researches (Friedlingstein et al., 2003). In the integrated model built with the 2nd subject of symbiosis, it is the research purpose of this subgroup to create the module which presumes the terrestrial ecosystem function about a carbon cycle. Although CO2 with the atmosphere has main breathing by photosynthesis by a plant, a plant, and edaphone, in order to reproduce a long-term ecosystem dynamic state, it is necessary to take into consideration the complicated various process in the inside of an ecosystem. It is rare to be solved about those physiological ecology-character, and although derivation of a general model leaves an experiential portion from a difficult thing, it aims at parameterization with few errors. Therefore, modeling is advanced, promoting the observation project and cooperation of symbiosis 3rd (terrestrial ecosystem) etc. Another purpose for spending of a terrestrial ecosystem model is giving the parameter related to land process, such as a water heat budget, from the simulation of a carbon dynamic state. Especially an important parameter is a leaf area index (LAI, leaf area per unit land area), and is used for presumption of the absorbed amount of solar insolation, or transpiration speed in a vegetation canopy. If LAI can be forecast in high accuracy through the carbon storage of a leaf from a terrestrial ecosystem model, it is expected that the prediction nature of the water heat budget in land can be raised. c. A research program, a method, and a schedule- FY 2002 - 2003The above-mentioned research purpose is most efficiently attained by linking Sim-CYCLE which is the existing terrestrial carbon cycle model, and the land process model MATSIRO (Takata et al., 2003). About the interaction of air-terrestrial, MATSIRO calculates water heat exchange and a photosynthetic rate based on LAI by Sim-CYCLE. Based on the amount of photosynthesis by the MATSIRO, Sim-CYCLE calculates many process inside ecosystems, such as distribution to each part of vegetation, consumption by breathing or withering to death, and decomposition in soil, (the soil temperature and soil moisture by MATSIRO are then taken into consideration). That is, it is that MATSIRO presumes the CO2 absorption to terrestrial from the atmosphere, and Sim-CYCLE presumes the CO2 discharge from terrestrial, and has a complementary relation of obtaining the net amount of exchange as the sum total. - FY 2003 - 2004The check of a model of operation is performed through the verification using various survey data. Verification in a small area base is performed [ 1st ] using the continuation observational data of the water, heat, and CO2 exchange between air-terrestrial by the ground observation group of symbiosis 3rd (terrestrial), the flux group of the Ministry of Environment synthesis promotion expense S1, etc. Various kinds of ecosystems are due to be applicable from a selva to the tundra there. The satellite observational data and the model point estimate of broad-based vegetation activity by the RIMOSEN group of symbiosis 3rd (terrestrial) etc. are compared [ 2nd ]. Comparison examination is due to be performed on all ball scales about items, such as LAI, absorptance of photosynthetically active radiation, and photosynthesis production of vegetation, there. The model which passed through verification plays the role which gives the climate-feedback through water, heat, and CO2 income and outgo in land by on-line in an integrative earth system model. The sensitivity analysis to which the response parameter to CO2 concentration of vegetation or temperature change is changed as numerical simulation, and the prediction experiment which set up a different CO2 discharge scenario of the artificial origin are conducted. - FY 2004 - 2006As a next stage, extension for taking structural change of a terrestrial ecosystem into consideration is performed. The more nearly actually near prediction experiment in consideration of composition change of the vegetable types (an evergreen broad-leaved tree, a shrub, single cotyledon herb, etc.) which constitute an ecosystem from linking with the vegetation distribution change model which the vegetation dynamic state group of symbiosis 2nd develops is conducted. It is made to converge on the synthetic model about MATSIRO, Sim-CYCLE, and terrestrial that linked the vegetation dynamic model. The prediction experiment by the integrated model which finally introduced the influence which a water heat budget-carbon balance-vegetation change in structuretextural change has on a climate system is conducted. d. The research program in FY 2002Existing ecosystem model Sim-CYCLE is rewritten in order to raise affinity with a climate model. Specifically, the original source code described by the C language is changed into a Formula Translator language. Simultaneously, it vectorizes to source code supposing the execution on vector computers, such as an Earth Simulator. In order to perform efficient calculation, the rate of vectorization of source code aims at 95% or more. It is parallel to the above-mentioned work, and the sensitivity experiment which inputs the prediction scenario of air CO2 concentration and a climate change into Sim-CYCLE of the C language version by off-line is conducted. A climatic prediction scenario uses what was obtained from the numerical simulation by the air-sea joint general circulation model (AOGCM) by the others and British Hadley center and the Canada climate center. [ CCSR/NIES / used as the physical climate core model of an integrated model ] An object period is from 1950 to 2099, the time series data of the climatic prediction experiment based on A2 and B-2 scenario by IPCC-SRES are inputted sequentially, and the response of the carbon balance of a terrestrial ecosystem is considered. For example, if the carbon storage of terrestrial will decrease in the future and it is emitted to the atmosphere, it will be guessed in the integrated model which combined the carbon cycle that warming is accelerated further. e. Reports in FY 2002The research program was followed and preliminary experiment was carried out with development of the terrestrial carbon cycle component which used existing model Sim-CYCLE supposing a link with a climate model as the base. e-1) The outline of a terrestrial carbon cycle componentModel Sim-CYCLE (Simulation model of Carbon cYCle in Land Ecosystems) used as the foundation is a model which evaluates productive capacity based on matter production theory. An ecosystem carbon cycle is calculated as in common with many models at Sim-CYCLE by the flow shown in Fig. 1. Namely, environment [ in / based on the input data which specifies conditions of location / each ecosystem ] (net radiation, soil moisture, etc.)
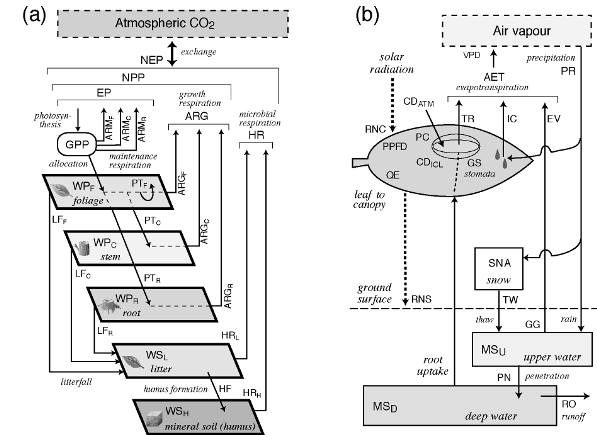
The structure and basic process of Sim-CYCLE were summarized to Table 1 and Fig. 2. The carbon cycle is simplified by five compartments and the flaw of 16 (figure 1a). However, in a prairie ecosystem, the carbon pool and flaw which became independent to each of a C3 plant and a C4 plant are set up. Net ecosystem carbon balance (NEP)
It comes out and asks (in autotrophy-breathing of vegetation, and HR, gross primary production and AR are [ GPP ] a soil reducer's heterotrophism-breathing). Conventionally, verification based on ecological investigation data is performed [ module / carbon cycle ] about the selva of Pasoh, the temperate evergreen broad-leaved forest in Minamata, the C3 / C4 synantectic prairie of a prairie, and the larch wood in East Siberia (Ito and Oikawa, 2002 references). The radiation and the water balance module in Fig. 1 are shown in figure 2b. Since it is expressed by carrying out the scale up of the leaf gas exchange, canopy process is stomata conductance. (Ball-Berry type model) It is controlled.
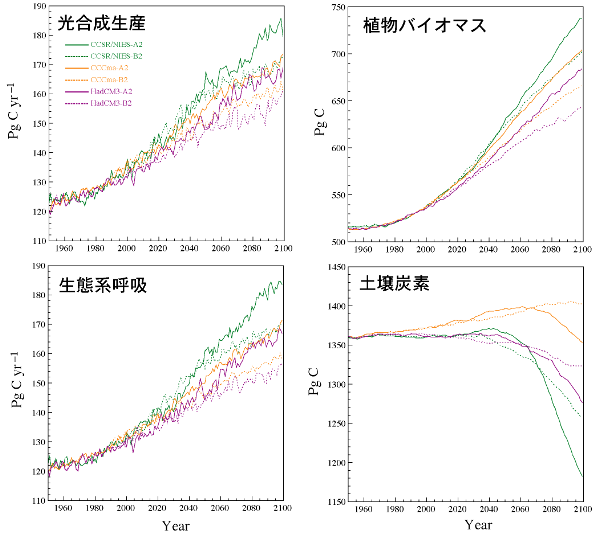
e-2)-1 Experiment setup All ball calculation is space. It carries out in a mesh for resolution power 30 minutes (about 55km), the meteorological condition and air CO2 concentration at the time of 1950 which carried out the long-term average (1961- 1998) of existing vegetation distribution of Olson and the NCEP/NCAR re-analysis are set up, and carbon balance is regular first. The state was searched for. Next, the climatic prediction scenario by the air sea joint general circulation model acquired from IPCC/deck decompression chamber was inputted into Sim-CYCLE, and the simulation which looks at a response on conditions without feedback through terrestrial carbon balance was performed. Making a computation time step into one month, 1950- 1989 assume the greenhouse-effect gas discharge scenario by IPCC-SRES air CO2 concentration and 1990- 2099 observed. e-2)-2 Experimental findingsWhile being, the annual pure primary productivity of a terrestrial ecosystem changed from 60 to 63 Pg C, the vegetation biomass changed from 515 to 530Pg C, and soil organic carbon was changing from 1360 to 1370 Pg C. The influence in which the fertilizing effect to photosynthesis the climate changes produced in this period are few, and according to an air CO2 concentration rise excelled was done (land use change is not taken into consideration). At this time, a difference significant to the trend of carbon balance between the scenarios by three kinds of used GCM(s) (CCSR/NIES, HadCM3, CCCma) is not seen. Air CO2 concentration increases in 1990 and afterwards to 621 ppmv by 847 ppmv and SRES-B2 scenario in SRES-A2 scenario. Corresponding to it, the mean temperature of all terrestrial showed 3-7-degree C warming, and response sensitivity differed fairly between GCM(s). In CCSR/NIES, the average precipitation of all terrestrial increased clearly, but others were changing by keeping things as they are. Geographicvariation clear to a climate change in any case occurred, the rise in temperature is remarkable in a high latitude region, and the regionality of an increase and reduction of precipitation was seen for every GCM. The trend of photosynthesis production of all terrestrial, ecosystem breathing (breathing of vegetation and a soil microorganism), the vegetable biomass, and soil organic carbon is shown in Fig. 3. Under the influence of the fertilizing effect by the air CO2 concentration rise which reaches the 1.7-2.4 present times, the photosynthesis quantity of production increased 30% or more, and the vegetable biomass showed the increase in a 110-200 Pg C thing. On the other hand, the increase in precipitation in an area promotes a microbial activity in part with a rise in temperature, the CO2 discharge from soil was accelerated, it is that it exceeds the withering-to-death thing supply from vegetation, and there was a case where a soil organic carbon reservoir was decreased. The tendency was notably seen especially in the scenario with large rise-in-temperature width. As a result, the whole carbon storage (= net income and outgo) became clear [ that the width of uncertainty is large from the thing (CCCma) used as large plus to what will be changed to minus from the second half of the 21st century ]. For example, in the subarctic forest in Eurasia, and an Amazon's selva, in spite of having been based on the air CO2 same scenario, a result which is as a result of [ presumed ] carbon balance, and is qualitatively different in addition to quantity between the scenarios by a climate model was obtained. e-2)-3 Sensitivity experimentAs a result of conducting the sensitivity experiment of controlling the experiment which fluctuated the parameter of a crack-per-pass, and a soil temperature rise about the soil organic carbon with which reduction in a storage was seen in the above-mentioned numerical simulation, it was suggested that the CO2 discharge from soil has influence strong against the carbon balance of the whole ecosystem (especially in the long run). This shows that it is necessary to propose to measure the character about soil decomposition preponderantly and to raise the accuracy of parameterization to future observation research.
f. ConsiderationSince the work planned in FY 2002 was attained mostly, the following fiscal year needs to carry out comparison verification which used survey data about the developed module. Although the fertilizing effect to the vegetation by air CO2 concentration rise and the facilitatory effect of the soil organic matter decomposition by a rise in temperature were remarkable in preliminary experiment, they are fields in which experimental and observation-research are done in the 3rd subject (terrestrial) of symbiosis. For example, since the exposure experiment to high CO2 concentration is conducted in the larch wood in Hokkaido, way of utilizing the result for model verification can be considered. It is thought that it is effective to perform comparison verification on the LAI data and the total ball levels by an artificial satellite, such as MODIS, over a very wide area. Moreover, if possible, terrestrial CO2 income and outgo will reproduce the influence which it has on the distribution between space-time which is air CO2 concentration by an air transportation diffusion model, and will perform top-down verification by comparing with observational data. On the other hand, it is necessary to advance extension about change (Foley et al., 2000) of the vegetation distribution which is not introduced into the present terrestrial ecosystem model, taking cooperation with a vegetation dynamic state group. There, although disturbance process, such as a competing process between plants and a fire, a still more nearly artificial land use change, etc. are applicable, when [ these ] a complicated phenomenon is adopted very much, it takes care so that uncertainty may not be made to expand. g. BibliographyFoley, J.A., S. Levis, M.H. Costa, W. Cramer, and D. Pollard, Incorporating dynamic vegetation cover within global climate models, Ecol.Appl., 10, 1620-1632, 2000.Friedlingstein, P., J.-L. Dufresne, P. Cox, and P. Rayner, How positive is the feedback between climate change and the carbon cycle, Tellus, 55B, 692-700, 2003. Ito, A., and T. Oikawa, A simulation model of the carbon cycle in land ecosystems (Sim-CYCLE): A description based on dry-matter production theory and plot-scale validation, Ecol.Model., 151, 147-179, 2002. Takata, K., S. Emori, and T. Watanabe, Development of the minimal advanced of the surface interaction and runoff, Glo.Plan.Change, in press, 2003. h. The announcement of a resultNext Page (1.2 Oceanic cycle model) |